Getting Started with Spring Data MongoDB using Java Configuration
In this tutorial, I'll show you how to use Spring Data MongoDB to integrate a MongoDB NoSQL database into a Spring Boot application. Spring lets you use either Java configuration or XML configuration or a mix of the two. I'll use a pure Java configuration.

In this tutorial, I'll show you how to use Spring Data MongoDB to integrate a MongoDB NoSQL database into a Spring Boot application.

I'll use these technologies and tools:
- Spring Tool Suite (STS) 3.8.4.RELEASE
- Java 8
- Spring Boot 1.5.3.RELEASE
- Maven 3.3.9
- MongoDB 3.3.4
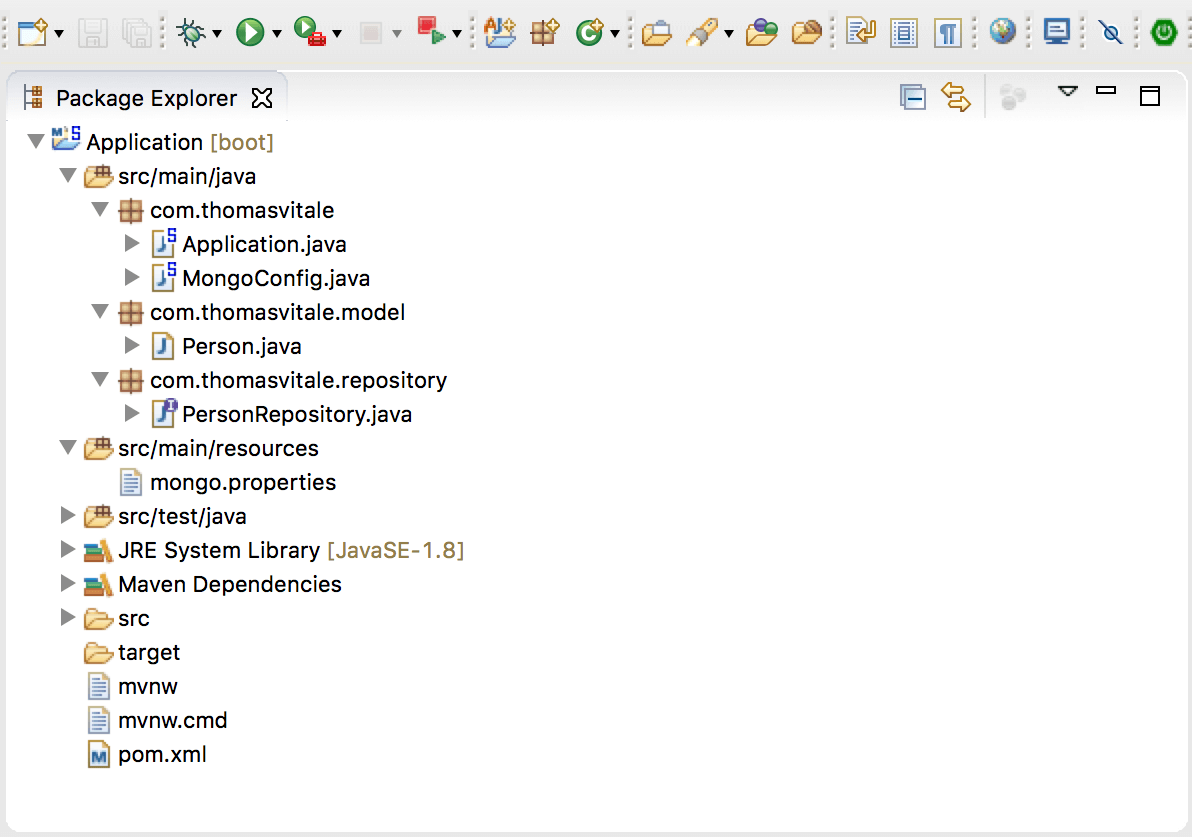
1. The Project Structure
The final folder structure of our project.
2. Create a new Spring Boot project
If you're using STS, you can create a starter project by either selecting File > New > Spring Starter Project from the main menu or right-click on the Package Explorer and choose New > Spring Starter Project.
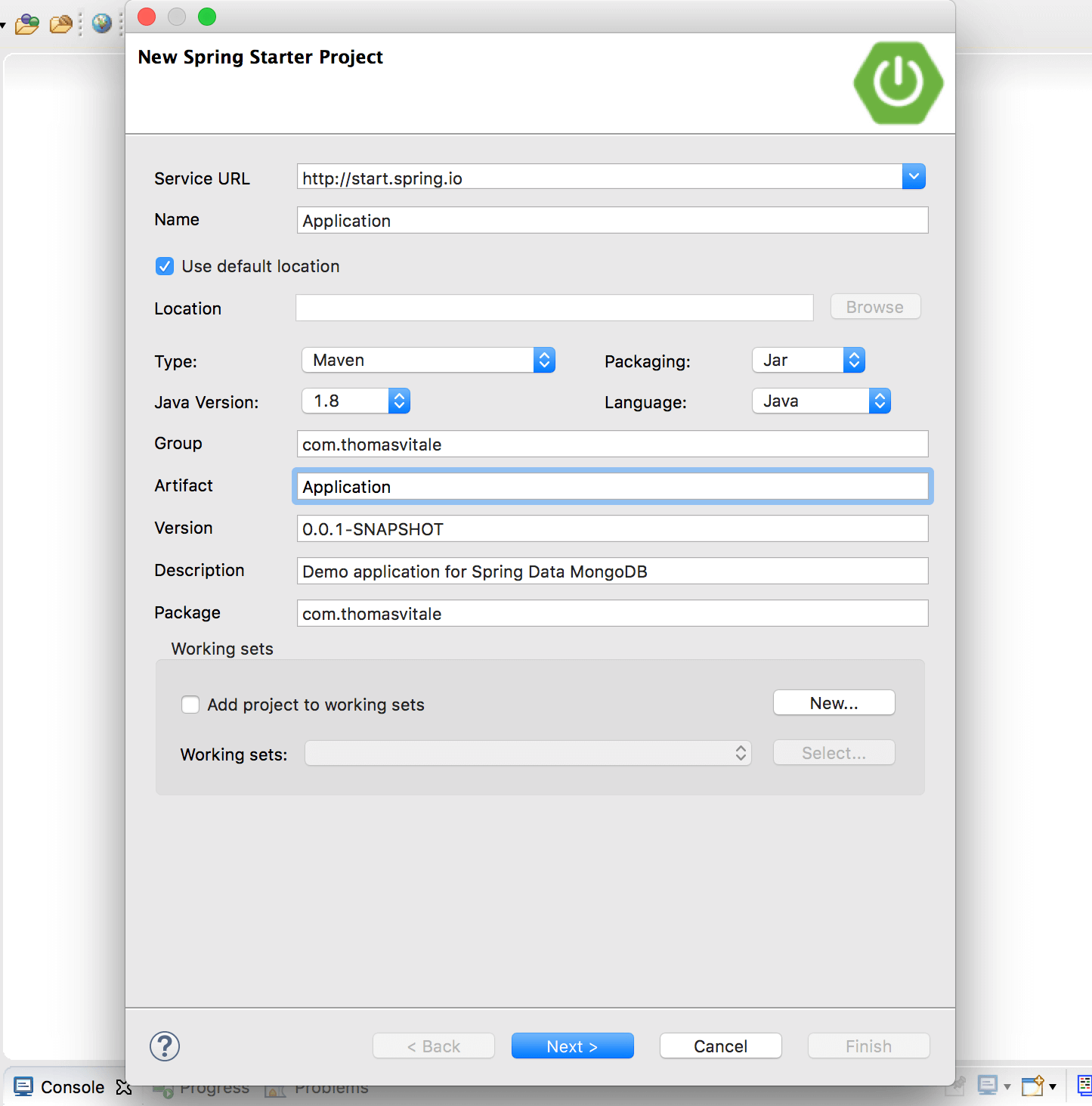
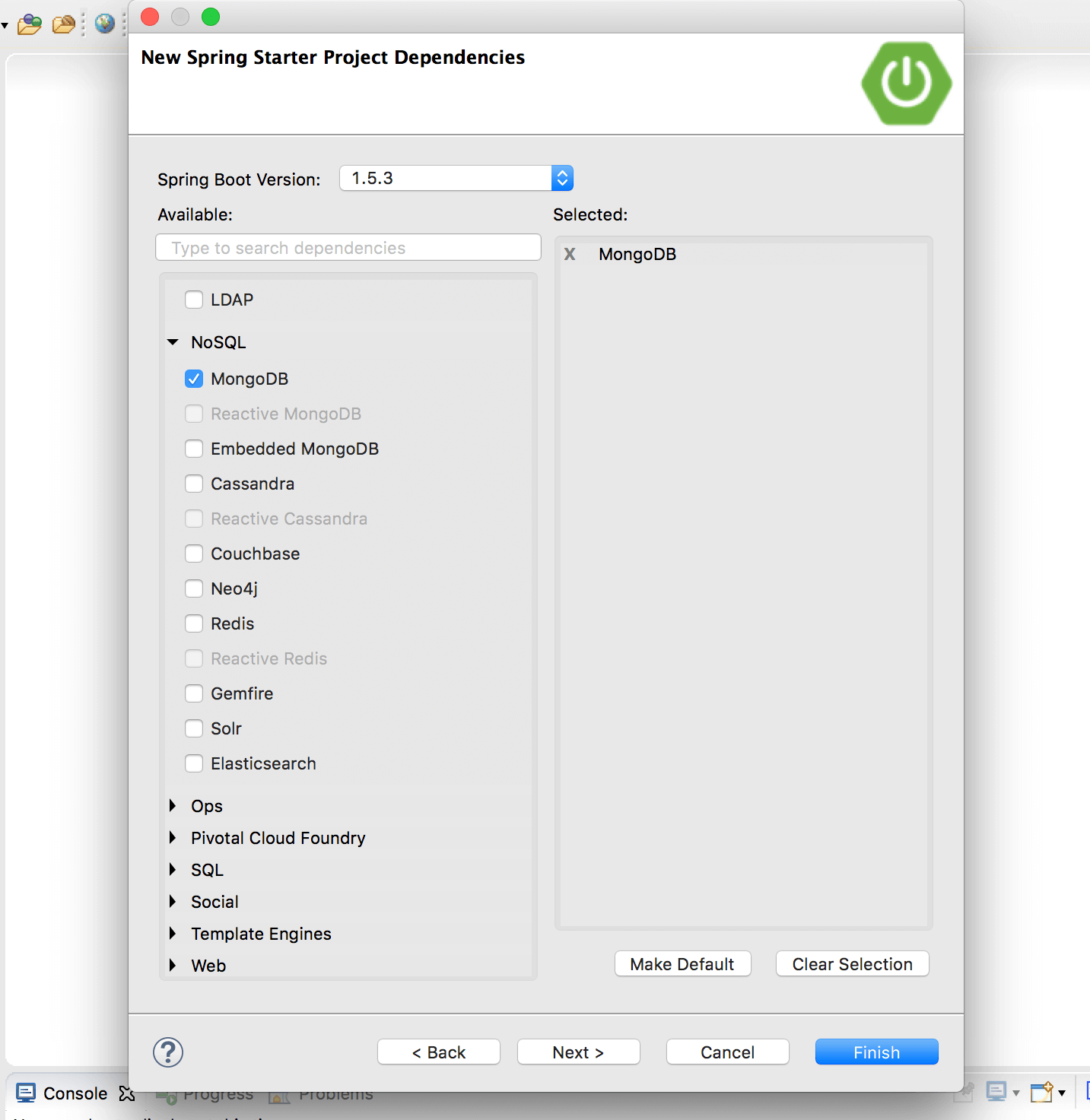
In case you're using another IDE like Eclipse, Netbeans or IntelliJ IDEA, you can create a new Maven project and add to the pom.xml file the dependencies listed in the next paragraph.
3. Maven Dependencies
spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb is the primary dependency of our project.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.thomasvitale</groupId>
<artifactId>Application</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>Application</name>
<description>Demo application for Spring Data MongoDB</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.3.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>4. Spring Configuration using Java Annotations
Spring lets you use either Java configuration or XML configuration or a mix of the two. I'll use a pure Java configuration
@Configuration
@EnableMongoRepositories(basePackages = "com.thomasvitale.repository")
@PropertySource("classpath:mongo.properties")
public class MongoConfig extends AbstractMongoConfiguration {
@Autowired
private Environment env;
@Override
protected String getDatabaseName() {
return env.getProperty("mongo.database");
}
@Override
public Mongo mongo() throws Exception {
return new MongoClient(env.getProperty("mongo.host"), Integer.parseInt(env.getProperty("mongo.port")));
}
@Override
protected String getMappingBasePackage() {
return "com.thomasvitale.model";
}
}and store MongoDB properties in a dedicated file.
mongo.database=mydb
mongo.host=127.0.0.1
mongo.port=327695. Person Model
The following is the Person Model. The @Document(collection = "persons") annotation specifies in which collection to store a Person document.
@Document(collection = "persons")
public class Person {
@Id
private String id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String firstName, String lastName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return firstName + " " + lastName;
}
}6. Person Repository
By extending MongoRepository, our PersonRepository has a lot of available operations, including the standard CRUD operations. You can also add custom operations like findByFirstName and findByLastName without writing any implementation: Spring Data MongoDB creates them for you!
public interface PersonRepository extends MongoRepository<Person, String> {
public Person findByFirstName(String firstName);
public List<Person> findByLastName(String lastName);
}7. Demo
Since we have Spring Data MongoDB configured, a model and a repository, it's time to test the application by performing some CRUD and custom operations.
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
PersonRepository personRepository;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
@Override
public void run(String... arg0) throws Exception {
// Save two Person documents on Mongo
personRepository.save(new Person("Sheldon", "Cooper"));
personRepository.save(new Person("Missy", "Cooper"));
personRepository.save(new Person("Leonard", "Hofstadter"));
// Get all people
System.out.println(">>> All people in the database:");
personRepository.findAll().forEach(System.out::println);
// Get all people with a specific last name
System.out.println(">>> All people with last name = 'Cooper'");
personRepository.findByLastName("Cooper").forEach(System.out::println);
// Update an individual person
Person person = personRepository.findByFirstName("Sheldon");
person.setFirstName("Shelly");
personRepository.save(person);
// Delete all
personRepository.deleteAll();
}
}Resources
- Spring Boot
- Building an Application with Spring Boot
- Spring Data MongoDB Project
- Accessing Data with MongoDB
- Spring Data MongoDB - Reference Documentation
If you're interested in cloud native development with Spring Boot and Kubernetes, check out my book Cloud Native Spring in Action.
